How it works
This section will work you through a brief overview of what web3 infras we are using and how they work together.
OS Composition
DataverseOS is similar to modern operating systems such as Linux, consisting of four important components
kernel, manages the underlying resources and ensures system stability & securitysystem calls, provides a set of APIs for applications to interact with the kernelprotocol drivers, an open architecture for 3rd-party protocol integrationuser interface, UI for users to interact with the system, manage their data, and use applications
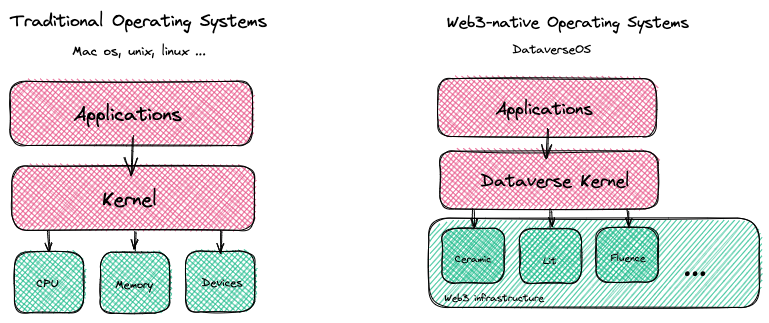
Plug into Dataverse
DataverseOS integrates and coordinates many protocols such as Ceramic (opens in a new tab), Lit Protocol (opens in a new tab), Lens Protocol (opens in a new tab), Filecoin (opens in a new tab) etc.
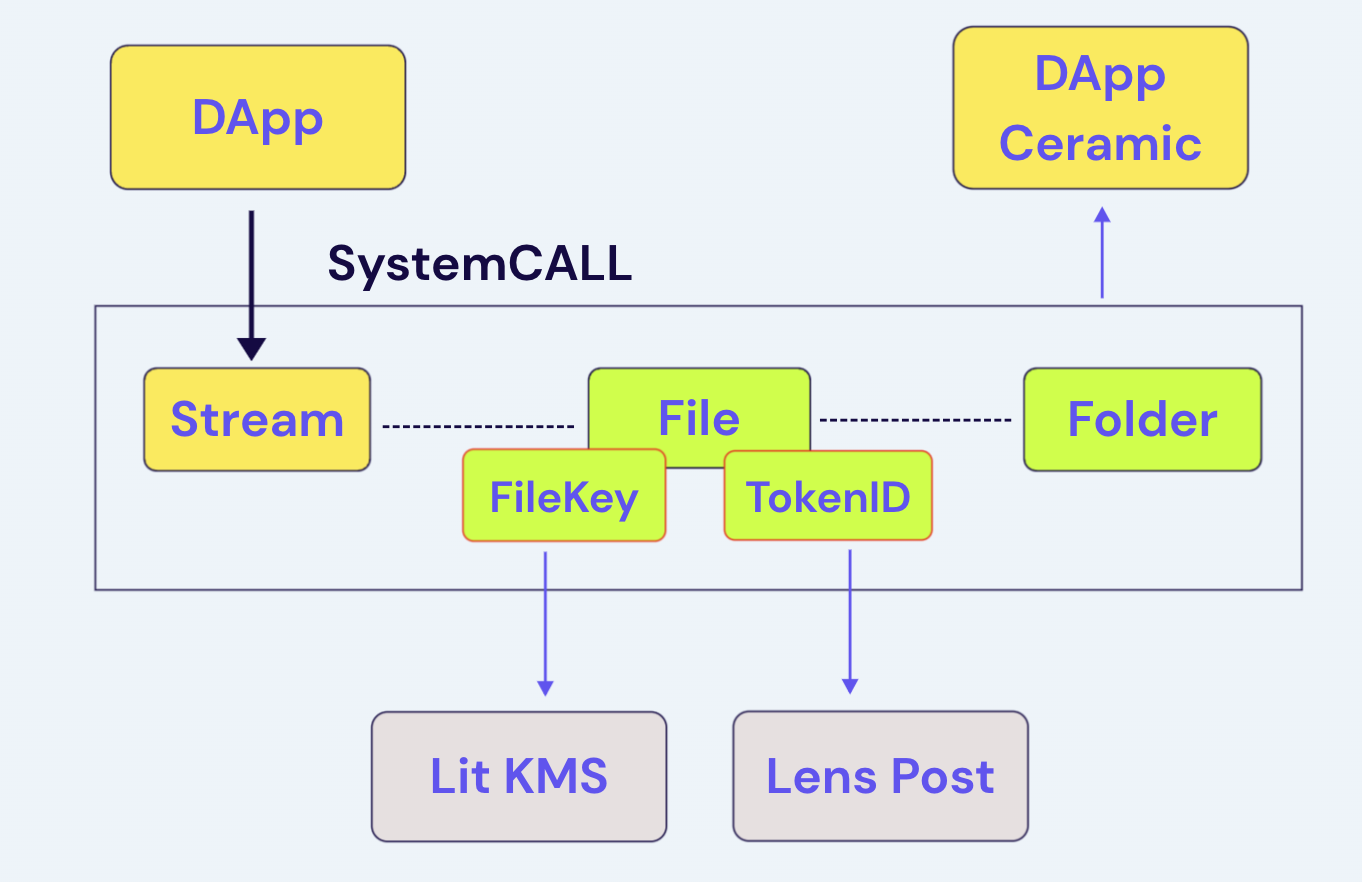
The encrypted file system is able to carry all files within DataverseOS over different applications by linking data streams on ceramic. Every time a data stream is created, DataverseOS will automatically create a corresponding file stream, bind the data stream to it and save it to the file system. Every byte of data is part of a file in DataverseOS. Users can manage their data via the file system.
On top of the file stream, DataverseOS fulfills programmability like access control by
integrating with Lit Protocol (opens in a new tab), allowing applications to build features like
permission management and data sharing flexibly.
Signature matters
DataverseOS, along with other latest data networks are building with EIP-4361 (opens in a new tab)
and EIP-5573 (opens in a new tab). These proposals are designed to standardize the way of user creating
identities, authenticating with applications, and managing data resources. In this context, Sign-In with Ethereum signature
is a complete proof of access rights to data resources. Therefore, it is important to keep the signature safe and secure.
For if the signature is stolen, the attacker can access the data resources and do all the bad things.
So we are building DataverseOS to take the duty of keeping everything safe and beyond the control of malicious applications.
How do we ensure security?
DataverseOS provides isolated data environments for each application. Each application has its own independent file system and scope of which data resources it can access. This scope will be specified clearly when the user is signing in.

User data will first be encrypted before putting in the file system. In other words, the applications will never see the raw data for all user data are encrypted.
When an application is requesting access to a data resource, the user will be notified and asked for permission. Specifically, the application will request the user to sign a message and declare which data resources it is accessing within that message.
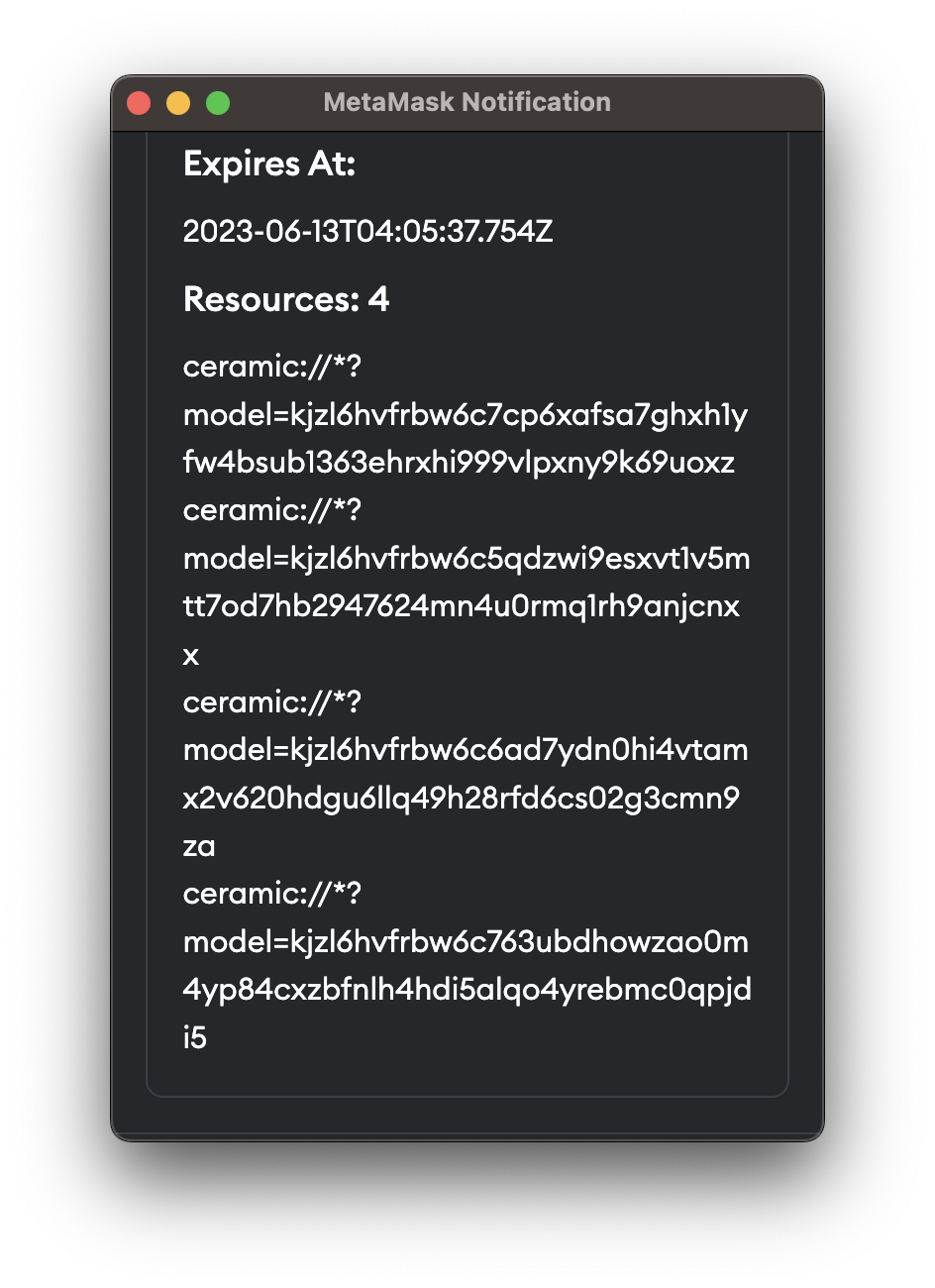
Before asking users to sign this message, the scope(A) and the message(B) will be checked first to ensure that B is a subset of A. If the request is valid, the application will be granted access to the data resource. Otherwise, the request will be rejected.
In summary, DataverseOS is able to protect data security by:
- Isolating data environments for each application
- Encrypting user data before putting it in the file system
- Checking the scope of data access requests to ensure the validity