Dataverse Cloud
Dataverse Cloud is decentralized, user-centric storage fully owned by your identity. A cloud drive to store, visualize and monetize all data assets.
Self-Sovereignty
Dataverse Cloud is a personal cloud drive where you truly own your data. Traditional cloud storage is centralised, with user data stored and calculated on someone else's servers. Dataverse Cloud is built upon decentralized data networks, where the user has the highest sovereignty over the data in the cloud drive. This sovereignty is reflected in the following aspects:
- The user decides who can access which data in the cloud drive
- The user can freely create, delete and update their own data, and even customize the functions they want through our SDK
- The user can profit from it instead of big companies profiting from it.
The product form of Dataverse Cloud is a Web Native File System(WNFS). It's an encrypted file system to save your digital footprints - creations, interests, contribution, social interactions, and more.

Hyper storage over applications
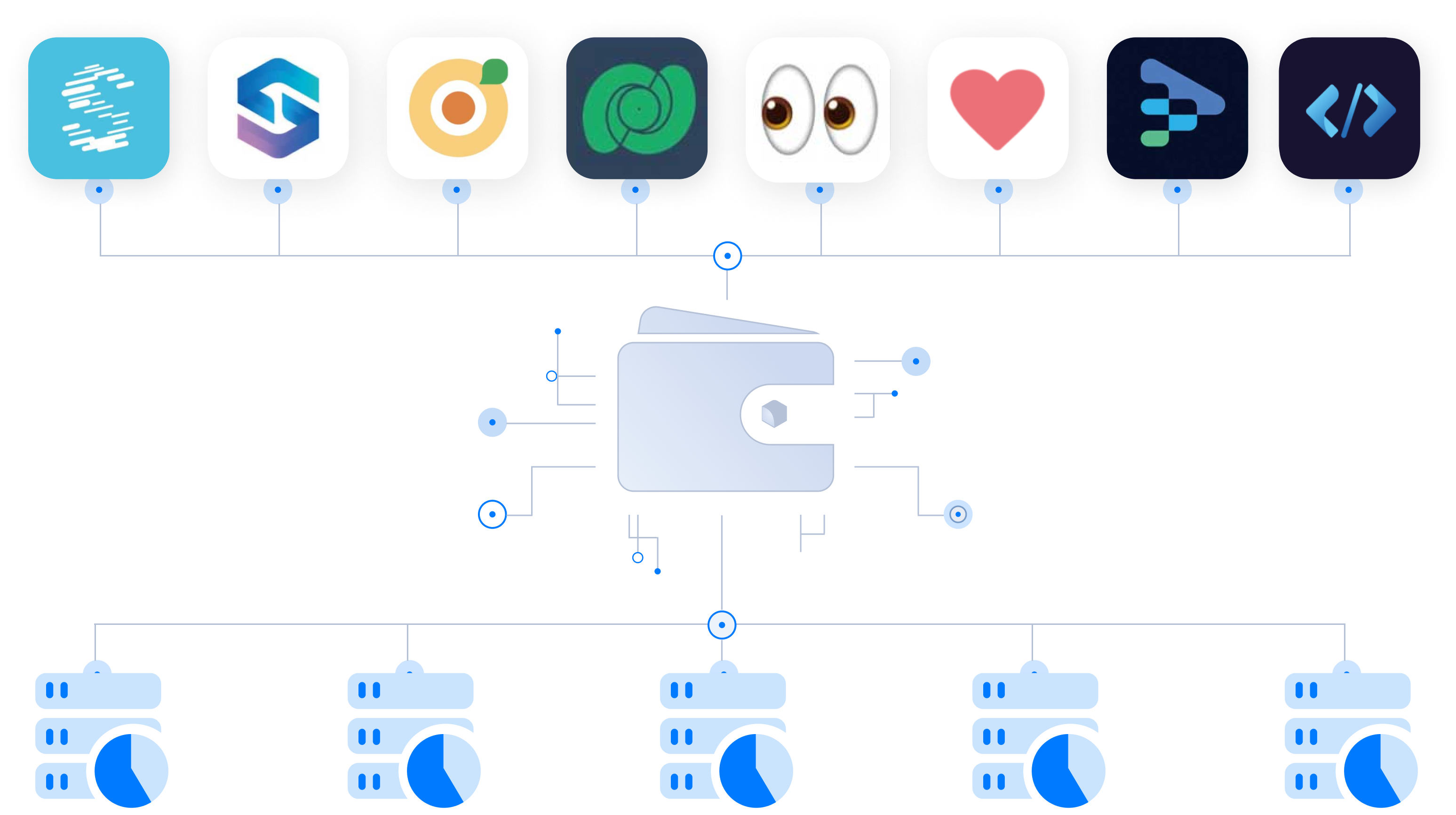
Dataverse Cloud is more than storage, it is also an open platform for application development. By providing SDKs to developers, we share the decentralized, secure, private, user sovereign storage capabilities of Dataverse Cloud with various decentralized applications. For example, a social app can store user profiles, social relationships, social content, etc. in Dataverse Cloud. While a note-taking tool can choose to save articles to Dataverse Cloud. With our SDK, everyone can build user-centric data applications on Dataverse Cloud.
For users, all the data generated from interacting with different applications will be aggregated in their own encrypted data space, no longer scattered across centralized companies' servers like isolated data islands as in the Web2 internet. Dataverse Cloud stores all of a user's data in one place, helping users reclaim ownership and value of their online data. At the same time, as a common data layer connecting thousands of applications, it provides interoperability between application data, under the premise of system security guarantees and user informed consent authorization.
Just like Google Drive powers Google Meet, Google Docs and other Google suite apps, where you can conveniently save recorded videos from Meet or documents from Docs to Drive, Dataverse Cloud will also provide users with a seamless experience of effortlessly commanding their data. The difference is Google Drive is closed and centralized, while Dataverse Cloud will be open and decentralized.
File sharing & monetization
Dataverse Cloud provides programmable file sharing and access control. Users can customize file accesses, such as setting whitelists or issuing NFT access tokens. Meanwhile, developers can freely program access conditions and rules.
At the same time, the native data monetization mechanism allows users to sell access to their data in the form of individual files (Data Token) or collections of files (Data Union). Developers can also build data economies on top of this, such as Web3 version of OnlyFans, Substack, data exchange marketplace, etc.
Why build Dataverse Cloud?
If we look back at the history of Data, we can divide it into three stages:
Stage 1: The invention of personal computer
During this time, we interacted with the software on our personal computers, and the data generated was stored on our hard disks. At that stage, we had actual control over our own data(no one else can steal data from our hard drive). However, the challenge was that it wasn't easy for others to access it. There was no effective means for sharing and facilitating data flow.
Stage 2: The emergence of the Internet
Subsequently, the advent of the internet completely transformed the landscape. Suddenly, data had the ability to flow seamlessly between various devices, granting us access to a plethora of captivating online resources. However, this marked the beginning of a shift where we gradually relinquished control over our own data due to the centralized nature of today's internet infrastructure. Presently, computing and storage predominantly occur in a centralized manner. Consequently, in this stage, we have willingly exchanged our data sovereignty for the unparalleled convenience offered by the internet.
Stage 3: The rise of Web3 era
Now, let's turn our attention to web3, the internet where data is computed and stored in a decentralized manner. The forthcoming generation of personal computers aims to combine the convenience of cloud computing with the security and privacy of a local PC.
In summary, we designed identity computer, the next generation of PC – decentralized, cloud-based, and self-controlled. Essentially, our system is designed by replacing traditional PC hardware components such as the CPU, memory, and hard disk with decentralized infrastructures, including blockchains, decentralized storage and databases. This change empowers us to restore complete control over data to the users.